 187
187
Variable-frequency Drive (VFD) is a power control equipment that applies frequency conversion technology and microelectronics technology to control AC motors by changing the frequency of the motor working power supply.
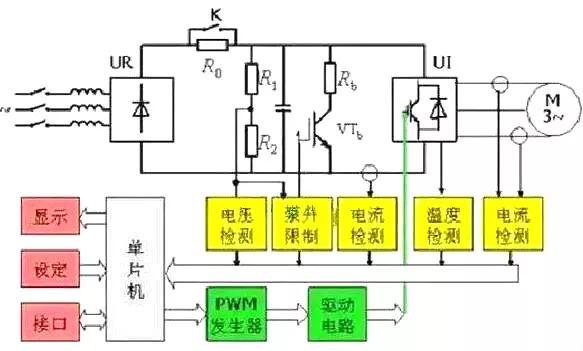
The frequency converter is mainly composed of rectification (AC to DC), filtering, inverter (DC to AC), brake unit, drive unit, detection unit, microprocessor unit, etc. The inverter relies on the internal IGBT to adjust the voltage and frequency of the output power supply, according to the actual needs of the motor to provide the power supply voltage it needs, so as to achieve the purpose of energy saving and speed regulation, in addition, the inverter has many protection functions, such as overcurrent, overvoltage, overload protection and so on. With the continuous improvement of industrial automation, frequency converters have also been widely used.
The basic composition of the frequency converter
Frequency converters are usually divided into 4 parts: rectifier unit, high-capacity capacitor, inverter and controller.
Rectifier unit: converts alternating current with a fixed operating frequency into direct current.
High-capacity capacitance: stores converted electrical energy.
Inverter: An electronic switch composed of an array of high-power switching transistors converts direct current into square waves of different frequencies, widths and amplitudes.
Controller: Work according to the set program, control the amplitude and pulse width of the output square wave, so that the superposition is an alternating current similar to a sine wave, and drive the AC motor.
Structure and schematic diagram of frequency converter
The development of the inverter also has to go through a gradual process, the initial inverter is not using this AC: AC to DC and then AC to AC topologies, but directly interchanged, no intermediate DC link. This kind of inverter is called alternating frequency converter, and at present, this kind of frequency converter has applications in ultra-high power and low-speed speed regulation. Its output frequency range is: 0-17 (1/2-1/3 input voltage frequency), so it cannot meet the requirements of many applications, and there was no IGBT at that time, only SCR, so the application range was limited.
The working principle of the inverter is to directly produce the required voltage conversion frequency power supply through several sets of phased switch control, its advantage is high efficiency, energy can be easily returned to the grid, its biggest disadvantage The highest frequency of the output must be less than the input power supply frequency 1/3 or 1/2, otherwise the output waveform is too poor, the motor produces jitter, can not work. Therefore, the alternating frequency converter has so far limited to low-speed speed regulation occasions, thus greatly limiting its scope of use.

Hotline:000-0000-0000
Tel:130 0000 0000
Email:22@22.cn
Address:Hangzhou West Lake District Zixia Street Internet Innovation and Entrepreneurship Park


